Portal:Africa



Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surface area. With nearly 1.4 billion people as of 2021, it accounts for about 18% of the world's human population. Africa's population is the youngest among all the continents; the median age in 2012 was 19.7, when the worldwide median age was 30.4. Based on 2024 projections, Africa's population will reach 3.8 billion people by 2099. Africa is the least wealthy inhabited continent per capita and second-least wealthy by total wealth, ahead of Oceania. Scholars have attributed this to different factors including geography, climate, corruption, colonialism, the Cold War, and neocolonialism. Despite this low concentration of wealth, recent economic expansion and a large and young population make Africa an important economic market in the broader global context. Africa has a large quantity of natural resources and food resources, including diamonds, sugar, salt, gold, iron, cobalt, uranium, copper, bauxite, silver, petroleum, natural gas, cocoa beans, and.
Africa straddles the equator and the prime meridian. It is the only continent to stretch from the northern temperate to the southern temperate zones. The majority of the continent and its countries are in the Northern Hemisphere, with a substantial portion and a number of countries in the Southern Hemisphere. Most of the continent lies in the tropics, except for a large part of Western Sahara, Algeria, Libya and Egypt, the northern tip of Mauritania, and the entire territories of Morocco and Tunisia, which in turn are located above the tropic of Cancer, in the northern temperate zone. In the other extreme of the continent, southern Namibia, southern Botswana, great parts of South Africa, the entire territories of Lesotho and Eswatini and the southern tips of Mozambique and Madagascar are located below the tropic of Capricorn, in the southern temperate zone.
Africa is highly biodiverse; it is the continent with the largest number of megafauna species, as it was least affected by the extinction of the Pleistocene megafauna. However, Africa also is heavily affected by a wide range of environmental issues, including desertification, deforestation, water scarcity, and pollution. These entrenched environmental concerns are expected to worsen as climate change impacts Africa. The UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has identified Africa as the continent most vulnerable to climate change.
The history of Africa is long, complex, and varied, and has often been under-appreciated by the global historical community. In African societies the oral word is revered, and they have generally recorded their history via oral tradition, which has led anthropologists to term them oral civilisations, contrasted with literate civilisations which pride the written word. During the colonial period, oral sources were deprecated by European historians, which gave them the impression Africa had no recorded history. African historiography became organized at the academic level in the mid-20th century, and saw a movement towards utilising oral sources in a multidisciplinary approach, culminating in the General History of Africa, edited by specialists from across the continent. (Full article...)
Selected article –

The African Union (AU) is a continental union of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the African Union. The bloc was launched on 9 July 2002 in Durban, South Africa. The intention of the AU was to replace the Organisation of African Unity (OAU), established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa by 32 signatory governments; the OAU was disbanded on 9 July 2002. The most important decisions of the AU are made by the Assembly of the African Union, a semi-annual meeting of the heads of state and government of its member states.
The AU's secretariat, the African Union Commission, is based in Addis Ababa. The largest city in the AU is Lagos, Nigeria while the largest urban agglomeration is Cairo, Egypt. The African Union has more than 1.3 billion people and an area of around 30 million km2 (12 million sq mi) and includes world landmarks such as the Sahara and the Nile. The primary working languages are Arabic, English, French, Portuguese, Spanish, and Swahili. Within the African Union, there are official bodies, such as the Peace and Security Council and the Pan-African Parliament. (Full article...)
Featured pictures –
Did you know (auto-generated) -

- ... that Malaysian businessman Lim Kok Wing was depicted as "King of Africa"?
- ... that before the swearing-in of convicted murderer Kenny Motsamai as an MP, South African Chief Justice Mogoeng Mogoeng cited a constitutional requirement prohibiting felons from becoming MPs?
- ... that Agri-Expo is the oldest agricultural society in Africa?
- ... that the pulse stops during the soliloquy of In C Mali?
- ... that Saint Augustine died during the Vandal conquest of Roman Africa?
- ... that South African singer Tyla delayed her debut album's submission date in order to collaborate with Tems?
Categories
Selected biography –
Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie (/ˌtʃɪməˈmɑːndə əŋˈɡoʊzi əˈdiːtʃi.eɪ/ ⓘ); born 15 September 1977, is a Nigerian writer and activist. Regarded as a central figure in postcolonial feminist literature, she is the author of the novels Purple Hibiscus (2003), Half of a Yellow Sun (2006) and Americanah (2013). Her other works include the book of essays We Should All Be Feminists (2014); Dear Ijeawele, or A Feminist Manifesto in Fifteen Suggestions (2017); a memoir, Notes on Grief (2021); and a children's book, Mama's Sleeping Scarf (2023).
Adichie was born and raised in Enugu. After her secondary education, she studied medicine and pharmacology for a year and half at the University of Nigeria. At 19, she left Nigeria for the United States to study at Drexel University, and would later study at three universities: Eastern Connecticut State University, Johns Hopkins University, and Yale University. She first published Decisions, a poetry collection, in 1997, which she followed with a play, For Love of Biafra, in 1998. She published Purple Hibiscus in 2003. Her father's story during the war supplied material for her second novel Half of a Yellow Sun. (Full article...)
Selected country –
 |
 |
||
| |||
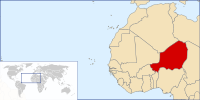
Niger, officially the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east. The capital city is Niamey.
At 1,267,000 square kilometres (489,000 sq mi), of which 300 square kilometres (115 sq mi) is water, Niger is the world's twenty-second largest country. Niger has a total of 5,697 kilometres (3,540 mi) of borders, the longest of which is with Nigeria to the south.
Niger's subtropical climate is mainly hot and dry. In the extreme south there is a tropical climate on the edges of the Niger River basin. The terrain is predominantly desert plains and sand dunes, with flat to rolling savannah in the south and hills in the north. The lowest point is the Niger River, with an elevation of 200 metres (722 ft) and the highest is Monts Bagzane at 2,022 metres (6,634 ft). (Read more...)
Selected city –
Bangui (French pronunciation: [bɑ̃ɡi]; or Bangui in Sango, formerly written Bangui in English) is the capital and largest city of the Central African Republic. It was established as a French outpost in 1889 and named after its location on the northern bank of the Ubangi River (French: Oubangui); the Ubangi itself was named from the Bobangi word for the "rapids" located beside the settlement, which marked the end of navigable water north from Brazzaville. The majority of the population of the Central African Republic lives in the western parts of the country, in Bangui and the surrounding area.
The city has been part of Bangui Prefecture since December 2020. As of 2020[update] it had an estimated population of 889,231. (Full article...)
In the news
- 17 January 2025 – Internal conflict in South Sudan
- Three people are killed and seven others are injured in clashes with security forces in Juba and Aweil, South Sudan, with three Sudanese-owned houses set on fire in Aweil. This comes after video emerged allegedly showing Sudanese soldiers killing South Sudanese civilians in Wad Madani, Sudan. (BBC News)
- 16 January 2025 – Somali Civil War, War against the Islamic State
- The Puntland Security Force claims to have captured a training facility used by ISIL militants, with over forty ISIL fighters killed following heavy fighting. (The Eastleigh Voice)
- Thousands of families are displaced as the military campaign intensifies, forcing locals to flee their homes in Bari region of Puntland, Somalia. (Idil News) (Horn Observer)
- 16 January 2025 – Red Sea crisis
- The leader of the Houthis Abdul-Malik al-Houthi announces that the group will monitor the implementation of the Israel–Hamas ceasefire agreement and continue its attacks on vessels and on Israel if the ceasefire is breached. (Middle East Monitor)
- 16 January 2025 – Sudanese civil war
- The U.S. Treasury Department sanctions the head of the Sudanese Armed Forces Abdel Fattah al-Burhan for "destabilizing Sudan and undermining the goal of a democratic transition" to a civilian-led government. (BBC News)
- 16 January 2025 – Stilfontein mine deaths
- The bodies of nine illegal miners trapped inside a gold mine in Stilfontein, South Africa, are recovered by police. (CTV News)
Updated: 3:05, 18 January 2025
General images -
Africa topics
More did you know –
- ...that Rukwanzi Island, an island in Lake Albert, one of the African Great Lakes, is the subject of a territorial dispute between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Uganda?
- ...that Oumarou Sidikou, vice-governor of the Central Bank of West African States from 1988 to 1993, was a minister in the government of Nigerien Prime Minister Hama Amadou, which was ousted by a military coup in 1996?
- ...that Jason Dunford, an All-Africa Games gold medalist and runner-up for the 2006 Kenyan Sportsman of the Year award, has a younger brother who was selected "most promising sportsman" at the same awards?
- ...that Sam Mbakwe, governor of Imo State from 1979 to 1983, served in the army of the Republic of Biafra, an Igbo secessionist state in southeastern Nigeria, during the Nigerian Civil War?
Related portals
Major Religions in Africa
North Africa
West Africa
Central Africa
East Africa
Southern Africa
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus